Warning
Please be advised this website is for internal review purposes only and is not to be distributed until advised.
Please be advised this website is for internal review purposes only and is not to be distributed until advised.
Thermal bridging is a term given to heat transfer through a conductive path that generally bridges insulation. Thermal breaks act to minimise heat transfer through the frame. The “R” rating refers to the degree of resistance to heat flow.
Under NCC compliance requirements for Energy Efficiency, thermal breaks with a minimum R-value of 0.2 are required for roofs and walls where the external lightweight cladding and internal lining are fixed to the same member eg wall stud or roof rafter. For roofs, lightweight cladding refers only to metal roof sheeting and for walls, includes weatherboards, fibre-cement and metal wall cladding.
Thermal breaks are not required when either the lightweight cladding or the lining is fixed to a secondary member (batten).
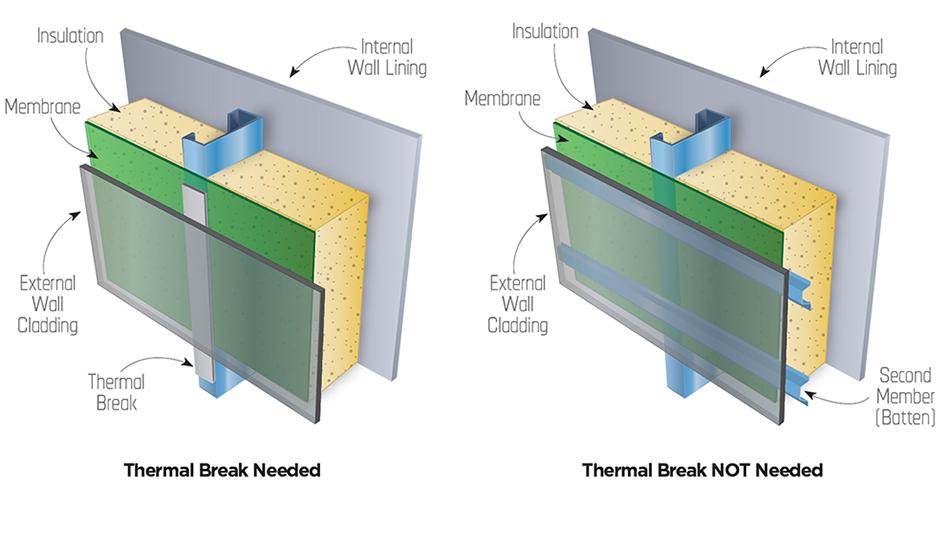
When an LGS frame construction involves lightweight external cladding (such as weatherboards, fibre cement or metal sheeting) there are two ways to achieve compliance.
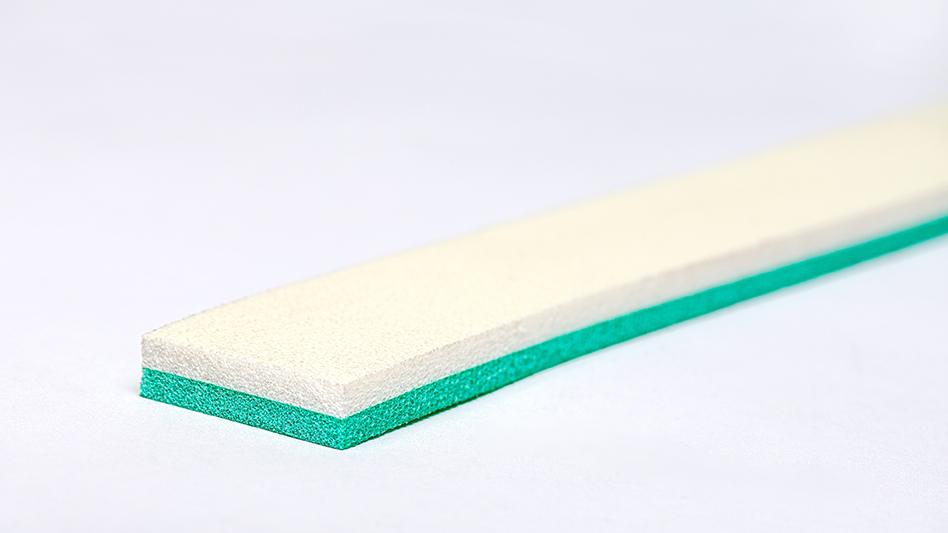
A proprietary thermal break with a minimum R-value of 0.2:
OR
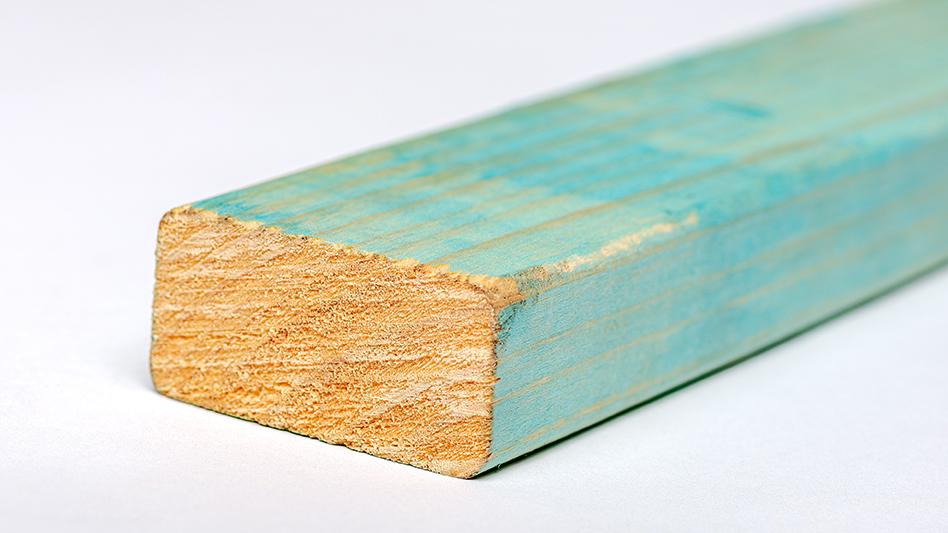
Min 20mm thickness battens from either metal or timber.
If fixing metal battens vertically, these should be fixed off stud (allow a 50mm minimum offset to parallel wall framing members) and secured to the top plate, bottom plate and noggins.

Steel framed brick veneer buildings do not require a thermal break because the air gap between the bricks and frame is considered sufficient. AAC and EPS cladding are other examples of products that don’t require a thermal break. Note that Insulated Sandwich Panels are not considered to be “lightweight cladding” and do not require a thermal break.
Vapour permeable wall membranes are generally recommended for LGS framing and these should be installed prior to the thermal breaks. Options for holding the wall membrane in place prior to fastening include double-sided tape, suitable LGS nail and washer etc.
Conventional pitched or truss roofs don’t require thermal breaks. However, thermal breaks are required for roofs with cathedral ceilings and skillion roofs, where the external metal sheeting is fixed on the same structural member as the internal lining. A roof thermal break with a minimum R-value of 0.2 needs to be built into the construction system design.
Using 20mm metal battens (installed perpendicular to the structural frame) is a recommended approach. This can also be a non-combustible solution for bushfire construction, zero lot boundaries and within 900mm of building allotment.
Alternative thermal break materials that are deemed suitable include:
Expanded polystyrene (min. 12mm thickness)

Product information for ATI Cavi-Break Strip® Thermal Break Strip
Hardie Break by James Hardie is a thick thermal break strip.
Product information for Kingspan's insulation product range

In this topic, we look at tips to erect wall framing such as positioning, orientation, fastening and joining